Health & Wellness
What Drives Alzheimer’s in Ladies?
Published
1 year agoon
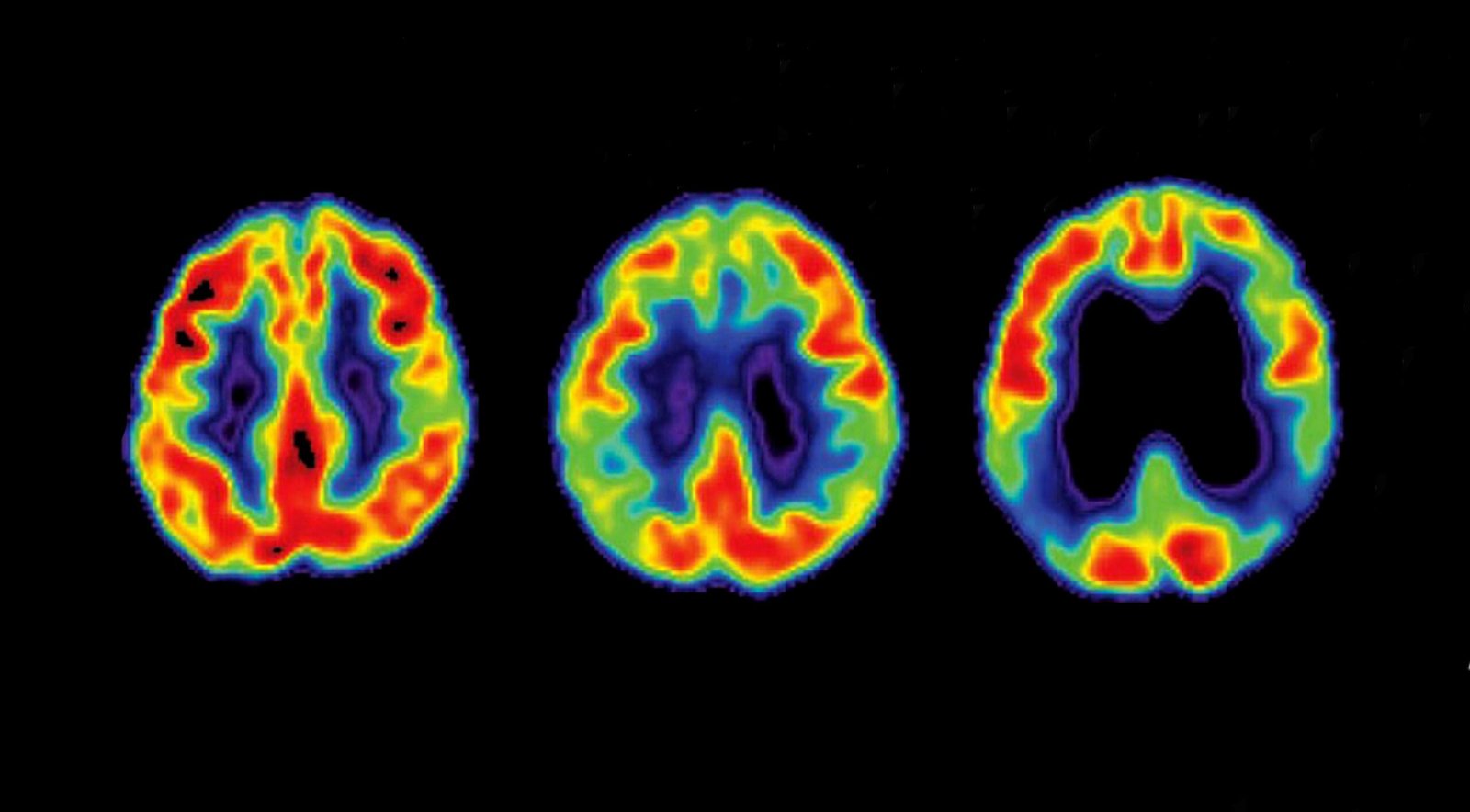
— Tau levels bigger when hormone remedy begins bigger than 5 years after menopause onset
by
Judy George, Deputy Managing Editor, MedPage This day
April 3, 2023
Female sex, early age at menopause, and hormone remedy use every had been connected to bigger regional tau in cognitively identical old folk with elevated beta-amyloid, unhealthy-sectional PET recordsdata confirmed.
The excellent levels of tau had been seen in hormone remedy users who had a prolong of bigger than 5 years between menopause onset and the initiating of hormone remedy, reported Rachel Buckley, PhD, of the Massachusetts Fashioned Health center in Boston, and co-authors in JAMA Neurology.
“Whereas a excellent-making an strive amount of stories contain targeted on the consequences of menopause and hormone remedy on risk of dementia, some distance fewer stories rigorously tested their association with Alzheimer’s illness biomarkers, namely amyloid and tau, in clinically identical old older ladies folk,” Buckley acknowledged.
“Here is serious to know given that it unruffled stays unclear what would be the driving mechanism of the menopause transition, and any use of hormone replacement, on risk for dementia,” she told MedPage This day.
“Counterintuitively, we stumbled on that women folk with elevated amyloid who reported taking hormone remedy furthermore confirmed bigger tau burden,” Buckley identified. “One would contain imagined taking hormone remedy would possibly perchance presumably well ameliorate the considerations with misplaced estrogen on fable of you are reintroducing estrogen into the physique.”
“But right here’s the put it got fascinating: after extra investigation into this neighborhood of girls folk who reported taking hormone remedy, we stumbled on that bigger risk used to be excellent connected to those ladies folk who had a protracted gap between their menopause onset and hormone remedy initiation — bigger than five or six years,” Buckley acknowledged. “Curiously introduction of exogenous estrogens after a protracted quit is now not a big belief.”
The findings add to an increasing physique of literature indicating that menopause — critically early or premature menopause — is a contributor to ladies folk’s bigger lifelong risk of Alzheimer’s illness, smartly-known Lisa Mosconi, PhD, of Weill Cornell Medication in Fresh York Metropolis, who wasn’t eager with the to find.
“This to find furthermore indicates that menopause hormone remedy would possibly perchance presumably well have an effect on some facets of Alzheimer’s pathology, per old proof that women folk who take grasp of hormones sincere thru the menopause transition or soon after would possibly perchance presumably well abilities bigger brain-protective advantages as when put next with folk who start taking hormones afterward in life,” Mosconi told MedPage This day. “General, the connection between menopause and Alzheimer’s illness has been overpassed for lots too long, despite its most likely significance.”
Premature menopause — that can presumably well furthermore be both spontaneous or the raze end result of surgical intervention forward of age 40 or forty five, respectively — occurs in 1% to 10% of girls folk and has been connected to worse dementia outcomes.
Early stories had urged that hormone remedy would possibly perchance presumably well ameliorate cognitive impairment in menopausal or postmenopausal ladies folk, Buckley and colleagues smartly-known. On the opposite hand, 2 decades within the past, the seminal Ladies’s Health Initiative (WHI) to find stumbled on that HT use used to be connected to approximately 2-fold bigger incidence of probable dementia relative to placebo, presumably attributable to initiating hormone remedy decades after menopause onset.
“In the case of hormone remedy, timing is the entirety,” co-author JoAnn Manson, MD, DrPH, who furthermore used to be a lead investigator on the WHI, acknowledged in a observation. “Our old findings from the WHI urged that starting hormone remedy early in menopause, reasonably than unhurried initiation, offers better outcomes for coronary heart illness, cognitive plot, and all-trigger mortality — and this to find suggests that the identical is factual for tau deposition.”
Buckley and colleagues broken-down recordsdata from the Wisconsin Registry for Alzheimer’s Prevention (WRAP), assessing PET scans of 292 cognitively unimpaired adults (193 ladies folk and 99 men) to search out out amyloid and tau levels in seven brain regions. Mean age used to be 67.4 at tau scan; 52 participants had extraordinary amyloid-beta and 106 had been APOE4 carriers. A total of 98 ladies folk had been previous or unusual hormone remedy users. Files had been peaceable between November 2006 and May perchance perchance 2021. Age at menopause and use of hormone remedy had been self-reported.
Amongst participants with elevated amyloid, female sex (standardized β=−0.41, P<0.001), earlier age at menopause (standardized β=−0.38, P<0.001), and hormone remedy use (standardized β=0.31, P=0.008) had been connected to bigger regional tau PET when put next with male sex, later age at menopause, and nonuse of hormone remedy. Medial and lateral regions of the temporal and occipital lobes had been affected.
Initiating hormone remedy bigger than 5 years after menopause onset used to be connected to bigger tau PET when put next with early hormone remedy (β=0.49, P=0.001). General findings remained after adjusting for years of education, APOE4, cardiovascular illness risk, menopause symptom severity, and menopause-connected sleep considerations.
The to find had lots of boundaries, Buckley and co-authors acknowledged. The researchers did not know what precipitated premature menopause or why ladies folk selected to start out hormone remedy; both elements would possibly perchance presumably well contain influenced the findings. As smartly as, most folk within the to find had been white.
-
Judy George covers neurology and neuroscience recordsdata for MedPage This day, writing about brain aging, Alzheimer’s, dementia, MS, uncommon ailments, epilepsy, autism, headache, stroke, Parkinson’s, ALS, concussion, CTE, sleep, anxiousness, and more. Apply
Disclosures
The WRAP to find is supported by the NIH.
Buckley is supported by a Pathway to Independence award and an Alzheimer’s Affiliation study fellowship. Co-authors reported relationships with the NIH, Fonds Nationwide de la Recherche Scientifique, WelBio, Biogen, Roche, Mars Edge, AC Immune, Alector, Genentech, Janssen, Neuraly, Oligomerix, Prothena, Renew, Alnylam, Cytox, JOMDD, NervGen, Neurocentria, Shionogi, Vigil Neuroscience, Ionis, Acumen, Vaxxinity, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Alzheimer’s Affiliation, Roche Diagnostics, and Cerveau Applied sciences.
Principal Source
JAMA Neurology
Source Reference: Coughlan GT, et al “Affiliation of age at menopause and hormone remedy use with common tau and β-amyloid positron emission tomography” JAMA Neurol 2023; DOI: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2023.0455.
You may like
Health & Wellness
Unanswered Questions: Dr. Sanjay Gupta Explores Trump’s Injuries Post Assassination Attempt
Published
2 days agoon
July 25, 2024
Nearly a week ago, a tragic incident occurred at a rally for Republican presidential candidate Donald Trump in Butler, Pennsylvania. Gunfire erupted, resulting in injuries to former President Trump, the unfortunate death of attendee Corey Comperatore, and severe injuries to two others.
Since the incident at Donald Trump’s rally where he was targeted, public images show him appearing largely unscathed and in good spirits. However, details from the campaign have been sparse regarding Trump’s medical condition, the care he received, and the ongoing monitoring by his medical team.
A comprehensive public evaluation of Trump’s injuries is crucial, both for his health and to provide transparency to voters about the potential future president’s recovery. Gunshot wounds near the head can result in unseen complications such as brain bleeding, inner ear damage, or psychological effects, which require thorough assessment. Drawing from my experience as a trauma neurosurgeon, I’ve witnessed how diligent evaluation post-injury can offer a clear prognosis and aid in a swift recovery.
The initial hour
The first official update on Trump’s health from his campaign arrived approximately 40 minutes after the shooting incident. It stated that Trump was reported as ‘fine’ and was undergoing evaluation at a local medical facility, with assurances that more information would follow.
About two hours later, Trump himself posted on Truth Social, revealing, ‘I was shot with a bullet that pierced the upper part of my right ear. I immediately sensed something was wrong upon hearing a whizzing sound and feeling the bullet tear through my skin.’
During his address at the Republican National Convention later that week, Trump recounted the moment of the shooting without providing additional details about his condition or treatment. Most of the public’s understanding of his injury stems from visual media and secondhand reports.
According to a source familiar with the situation speaking to CNN on Sunday, Trump underwent a series of ‘routine’ tests at the hospital, including a CT scan that yielded normal results.
Despite repeated attempts by CNN to obtain further information from the Trump campaign and Butler Memorial Hospital, details regarding Trump’s condition and ongoing care remain limited. CNN continues to seek comment from the Trump campaign as of Thursday.
Insights into Trump’s Injury
Following the gunfire on Saturday, Trump reacted by raising his right hand to his ear and face. Despite visible blood, he remained conscious and responsive, voluntarily lowering himself to the ground before quickly rising to his feet within moments, with the support of US Secret Service agents surrounding him. Shortly after, he stood, raised his right arm, and actively engaged with the audience, encouraging them to ‘Fight!’ while pumping his fist in the air. These actions, viewed from a medical perspective, indicate positive signs of his condition, suggesting he was not severely injured.
US Rep. Ronny Jackson, Trump’s former White House physician, shared in an interview on Monday’s ‘The Benny Show’ podcast that he personally assessed and bandaged the wound to Trump’s ear. He clarified that the bullet, which did not cause a concussive effect due to its distance from Trump’s head, grazed the top of his ear, resulting in significant bleeding.
After the incident, Trump was swiftly transported to nearby Butler Memorial Hospital. Dr. David Rottinghaus, an emergency room physician at the hospital, confirmed that they had coordinated with the Secret Service ahead of the rally. While Rottinghaus did not treat Trump directly and refrained from commenting on his specific treatment or condition, he highlighted the hospital’s preparedness for such emergencies.
‘We do prepare for incidents like this. We’ve had advanced visits and coordinated plans with the Secret Service and law enforcement in anticipation of potential crises,’ Rottinghaus told CNN. These preparations included reserving an ER bed, deploying clinical teams at the rally venue to handle minor medical issues on-site, and ensuring the hospital was not overwhelmed during any crisis.
When the unexpected occurred, Rottinghaus stated that Butler Memorial Hospital swiftly implemented its emergency plan, securing the facility and redirecting patients to other healthcare providers.
Details surrounding Trump’s medical evaluation remain unclear, including the timing of his CT scan and other tests, the interpretation of these scans, and whether specific examination of his brain was conducted.
In a Monday interview, Jackson reassured that Trump’s wound was dressed and anticipated to heal naturally without further intervention. He expressed confidence in Trump’s recovery, stating, ‘It’s going to heal and granulate on its own.’
Later in the week, Eric Trump mentioned in an interview with CBS News that his father did not require stitches but sustained a significant flesh wound. Despite the injury, Trump has been actively participating in the Republican National Convention in Milwaukee, delivering speeches with a visible bandage on his ear while engaging with attendees.
What remains uncertain
All indications suggest a positive outlook. Yet, there’s a notable absence of detailed information regarding the precise diagnosis and treatment of what could have been a severe injury. While the focus has centered on his ear and the right side of his head, potential additional injuries cannot be ruled out. There remains uncertainty about whether he was hit by a direct projectile from the rifle, a secondary projectile, or a combination thereof. Such distinctions often require thorough assessment to ascertain.
The weapon used by the shooter was identified as an AR-15-style firearm, known for its significant kinetic energy. In my surgical experience, I’ve seen the kind of trauma such weapons can inflict, especially in proximity to the head, where they can cause unseen injuries.
These may include fractures to the delicate skull bones, epidural hematomas (bleeding between the skull and brain), and damage to the inner ear bones, potentially leading to hearing loss, vertigo, or dizziness. While a CT scan is typically used to detect such injuries, they may not always be immediately apparent, necessitating close monitoring and possibly repeat scans during hospital observation.
Dr. Kenji Inaba, a trauma surgeon from the Keck School of Medicine, underscores the delayed onset of psychological impacts following such traumatic events. He emphasizes the importance of ongoing vigilance in recognizing and addressing these issues.
While most physical symptoms of an injury typically manifest within days, the Trump campaign has not disclosed whether a comprehensive evaluation was conducted initially or if there has been subsequent follow-up.
While presidents and presidential candidates are not obligated to disclose their medical histories, voters have consistently expressed that the health of their leaders is a significant consideration in elections. Access to more information enables informed decision-making for all.
Dr. Rottinghaus, the physician from Butler Memorial, acknowledged that despite thorough preparation, Saturday brought unexpected challenges. Nevertheless, he described the day as successful due to effective communication, clear planning, and readiness to respond promptly.
Amidst a heightened political climate, this collaborative approach and emphasis on communication could serve as a valuable lesson for candidates as they navigate the rigorous demands of the campaign trail.
Health & Wellness
Study Reveals Long Covid Risk Decreases Over Time but Still Significant
Published
1 week agoon
July 19, 2024
In the midst of a summer wave of COVID-19 infections across the nation, a timely study has delved into the evolving risk of long Covid and its trajectory over the course of the pandemic.
Research findings indicate that while the likelihood of developing long-term COVID-19 has diminished since the onset of the pandemic, it remains substantial, particularly among individuals who have not received vaccination against the virus.
A recent analysis by the federal Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, published in June, revealed that approximately 7% of American adults—equivalent to about 18 million people—have experienced long Covid. Harvard economist David Cutler estimated in 2022 that the total cost of long-term COVID-19 to the nation amounted to $3.7 trillion, representing 17% of the country’s pre-Covid gross domestic product.
Published on Wednesday in the New England Journal of Medicine, the new study draws on extensive data mining and advanced machine learning techniques applied to millions of medical records from the Department of Veterans Affairs. It suggests that both the human and financial impacts of long COVID-19 are likely to continue growing.
Researchers from Washington University in St. Louis and the VA Health System conducted a comprehensive study to assess how the risk of lingering symptoms related to long-term COVID-19 has evolved throughout different phases of the pandemic, considering varying COVID-19 variants and vaccination statuses.
The study, which included over 441,000 individuals who contracted COVID-19 between March 2020 and January 2022 and lived at least 30 days after infection, compared their medical records with more than 4.7 million people who visited the VA for reasons unrelated to COVID-19 during the same period.
Initially, during the first year of the pandemic with the ancestral coronavirus strain and limited immunity, approximately 1 in 10 Covid-19 patients developed symptoms consistent with long Covid within a year of their initial infection.
The introduction of vaccines marked a significant shift, halving the risk of long-term COVID-19 during the Delta variant wave in the summer of 2021. However, for those unvaccinated during this period, around 10% continued to experience lingering symptoms post-infection.
With the Omicron variant’s emergence in late 2021, the study found that 3.5% of vaccinated individuals developed long-term COVID-19 after the acute phase, compared to 7.7% of those who remained unvaccinated.
The study’s findings are limited by its predominantly White male VA patient population, which may not fully represent the diversity of the general public. For instance, recent research indicates a potentially higher incidence of long-term COVID-19 among pregnant individuals compared to the broader population.
These insights highlight the complex interplay between Covid-19 variants, vaccination status, and the risk of long-term symptoms, underscoring ongoing challenges and areas for further investigation in managing post-Covid health outcomes.”
The recent study from Washington University and the VA Health System underscores the evolving understanding of long-term COVID risk amidst changing COVID-19 variants and vaccination efforts. However, it leaves some important considerations unexplored.
Notably, the study does not differentiate between individuals who received only their primary series of COVID-19 vaccines and those who also received recommended booster shots to maintain immunity against evolving virus strains. Additionally, it does not delve into the potential impact of natural immunity acquired from prior infections, an area of interest for future research according to Dr. Ziyad Al-Aly, the senior study author.
Dr. Al-Aly estimates that approximately three-quarters of the observed decrease in long Covid risk since the early stages of the pandemic can be attributed to the widespread vaccination efforts. Vaccines play a crucial role in aiding the immune system to suppress viral load and clear the virus more effectively, potentially reducing the persistence of active virus thought to contribute to long Covid symptoms.
Dr. Hector Bonilla from Stanford’s Post-Acute Covid-19 Syndrome Clinic emphasizes the pivotal role of vaccination in mitigating long-term COVID-19, noting a significant decline in new cases of lingering symptoms among vaccinated individuals compared to earlier stages of the pandemic.
However, despite these advancements, the study underscores that around 3 out of 100 vaccinated individuals who contract COVID-19 may still develop long-term COVID-19, highlighting the ongoing substantial risk. This risk, though reduced, remains a significant concern for public health experts like Dr. Daniel Griffin from Columbia University, who stresses the persistent impact of long-term COVID-19 on individuals’ health and well-being.
As the virus continues to evolve, both through vaccination and changes in the virus itself, understanding and addressing the complexities of long Covid remain critical priorities in managing the broader health outcomes of the pandemic.”
“Despite a decrease since the early days of the pandemic, new cases of long Covid continue to emerge, highlighting ongoing challenges in patient care and treatment development.
Dr. Al-Aly emphasizes that this study and others underscore the critical need for increased funding and coordinated care for long Covid patients. He stresses the urgency for further research into effective treatments.
“I don’t believe the US is sufficiently addressing this problem,” Dr. Al-Aly stated. “While there’s a desire to move forward, millions of people are still suffering from long Covid, and unfortunately, more will continue to do so even with declining numbers.”
“There’s currently no comprehensive plan to tackle this issue,” he added firmly, “and that’s unacceptable.”
Health & Wellness
Inside the Debate: Should President Biden’s Cognitive Health be Tested? Dr. Sanjay Gupta Weighs In
Published
3 weeks agoon
July 8, 2024
When President Joe Biden stepped onto the debate stage last week, it was evident from his opening remarks that his performance would not meet expectations. As a specialist in neurology, I found it troubling to observe, and I wasn’t alone in this sentiment. In the days following the debate, I received numerous communications from fellow medical professionals specializing in brain health. While the observations we made weren’t entirely novel, the extent of their prominence right from the debate’s outset raised concerns.
From a neurological perspective, our concerns stemmed from his disjointed speech patterns, abrupt lapses in concentration mid-sentence, hesitant speech, and lack of facial expressiveness, occasionally leading to a blank, open-mouthed look. It’s important to clarify that these are observations and not indicative of any deeper diagnosis. None of the medical professionals involved intended to imply otherwise.
Medical Consensus Urges Comprehensive Cognitive and Movement Disorder Testing for President Biden, Experts Say Public Disclosure Necessary
In light of recent discussions among medical professionals specializing in neurology, there is a growing consensus that President Biden should undergo thorough cognitive and movement disorder testing. The results of these tests, they argue, should be transparently shared with the public.
Having extensively covered advancements in dementia treatment over the past five years, including Alzheimer’s disease, Lewy body dementia, and vascular dementia, I have firsthand experience with the rigorous testing protocols involved. For my documentary “The Last Alzheimer’s Patient,” I underwent comprehensive cognitive assessments, examining aspects such as executive function, judgment, and memory, alongside blood tests to measure brain protein levels and B12 levels, as well as genetic risk factors and sense of smell assessments. While such testing isn’t typically routine for most individuals, every neurologist I consulted emphasized its importance in President Biden’s case.
Biden’s Medical Background: A Closer Look
The most recent official health summary released in February affirmed President Biden’s fitness for duty, compiled by a team of 20 doctors, including a neurologist, who conducted a thorough physical examination. According to the summary, an extensive neurologic evaluation found no signs consistent with neurological disorders, and there was no indication of Parkinson’s disease to explain symptoms like stiffness and reduced facial expression.
However, the report did note findings of neuropathy and arthritis in his feet, conditions that can cause numbness, weakness, and discomfort. Notably absent from the report was any mention of cognitive testing, raising questions about whether such evaluations have been conducted.
Following a recent debate where concerns about Biden’s cognitive performance arose, the White House stated that a subsequent medical check, prompted by a cold, was brief and not a full physical examination. When pressed about the necessity of cognitive testing results, White House press secretary Karine Jean-Pierre indicated that Biden’s medical team deemed it unnecessary.
These developments underscore ongoing discussions and uncertainties surrounding President Biden’s health disclosures and the extent of medical evaluations conducted.
Both President Biden, at 81, and former President Donald Trump, at 78, have exceeded the average American male lifespan of 74.8 years, a testament partially attributed to their access to top-tier healthcare and abstention from drinking and smoking. Biden’s medical history includes two brain surgeries for aneurysms, with the rupture of one on the left side potentially posing a risk for delayed cognitive issues later in life. Conversely, Trump, whose father suffered from Alzheimer’s disease, lacks other known risk factors for cognitive decline.
Trump, who has occasionally exhibited similar cognitive signs to Biden such as nonsensical speeches and confusion over names and current events, claimed to have aced the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) in 2018, with subsequent exams in 2023 reportedly showing exceptional results, according to Dr. Bruce Aronwald. However, Trump has not disclosed his full medical records, and past health memos have used atypical language for medical documentation.
While the MoCA serves as a preliminary screening tool, experts emphasize a more comprehensive cognitive evaluation for Biden, suggesting it could provide valuable baseline data for assessing cognitive changes. The absence of such a baseline examination for Biden raises questions about the thoroughness of his cognitive health assessments compared to Trump’s documented tests.
Episode or Condition: Understanding the Difference
According to Jay Olshansky, a professor at the University of Illinois-Chicago’s School of Public Health, older individuals often possess a form of intelligence known as crystalized intelligence. This encompasses accumulated wisdom gained through learning and life experiences, which can be particularly valuable in roles such as the presidency.
As we age, certain cognitive abilities like processing speed, attention span, and memory may naturally decline. This is a normal part of aging and typically doesn’t hinder someone’s ability to perform their job. However, for a minority, this decline can be more pronounced and may indicate conditions like dementia, where the distinction lies between forgetting where you placed your keys and not comprehending their purpose.
Diagnosing dementia isn’t straightforward and other factors, such as poor sleep, low blood sugar, viral illnesses, or medications, can contribute to temporary cognitive impairment, often referred to as brain fog.
Recently, after a debated performance, Biden’s aides attributed his performance to a ‘bad night’ compounded by a cold, without medication. White House spokesperson Karine Jean-Pierre noted Biden’s jet lag and late-night presidential duties and debate preparation. Following discussions with Democratic governors, Biden adjusted his schedule to end events by 8 p.m. to prioritize sleep, an effort to manage fatigue from the late-night debate start at 9 p.m. Eastern time.
Seeking Clarity: Finding Answers
As the November election approaches, questions linger about President Biden’s health without definitive answers. The White House has declined press requests for additional medical records and interviews with Biden’s physician, Dr. Kevin O’Connor. According to Biden’s press secretary, Dr. O’Connor observed the debate and had no post-event concerns.
Like all citizens, elected officials are entitled to privacy regarding their medical information under federal healthcare laws. There is no legal provision for accessing personal medical details without authorization, even for the president, and disclosure of such information is not mandatory for presidential candidates. Over my 23 years of reporting on these matters, only Senator John McCain, one of the oldest presidential candidates in US history, chose to share his complete medical records with both myself and the American public.
The belief that observing a candidate on the campaign trail provides the best insight into their physical and cognitive health is commonly held. In 2020, Biden himself asserted that the rigorous demands of running for president were a constant test of his capabilities, stating, “All you’ve got to do is watch me.”
As the nation watches now, concerns have arisen from this assessment, prompting a clear call for transparent testing to address these concerns definitively.
Health & Wellness
Navigating the Controversy: Insights into New Alzheimer’s Criteria and the Debate Over Diagnostic Creep
Published
4 weeks agoon
July 2, 2024
As a new Alzheimer’s treatment awaits approval, the Alzheimer’s Association has released its updated diagnostic criteria, emphasizing the use of biomarkers like beta amyloid and tau proteins detected through lab tests or brain scans. This marks a significant shift from traditional pen-and-paper memory and thinking assessments in disease diagnosis.
The rationale behind these changes, according to the authors, is to detect Alzheimer’s in its earliest and potentially more treatable phases, possibly before symptoms manifest. However, this approach also raises concerns that individuals could receive an Alzheimer’s diagnosis based solely on a blood test, regardless of whether they exhibit memory impairments.
The authors advocate for a biological basis for diagnosis, emphasizing that symptoms alone should not determine Alzheimer’s diagnosis. They argue that individuals without current symptoms could still develop them in the future.
However, critics, including external experts and drug industry watchdog groups, argue that beta amyloid proteins can be present in the brain and blood without leading to dementia symptoms. They also highlight the lack of evidence supporting the efficacy of costly and potentially risky injected medications administered before symptom onset for long-term benefits.
Balancing the Pros and Cons of Early Diagnosis
In clinical trials, the new drugs — antibodies targeting beta amyloid to clear brain plaques — demonstrated moderate benefits. Beta amyloid peptides are protein fragments that accumulate into sticky brain plaques, often alongside tau protein, which forms tangles disrupting nerve cell communication, both hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease.
Debate Continues Over Beta Amyloid’s Role in Alzheimer’s Disease, Some Experts Suggest Plaques Are a Result Rather Than a Cause
In an 18-month study involving individuals in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease, the FDA-approved antibody lecanemab slowed cognitive decline by 27% compared to a placebo. Similarly, the experimental drug donanemab showed a 35% reduction in disease progression compared to placebo last year, leading an FDA advisory group to recommend its approval for Alzheimer’s treatment. However, these drugs carry risks such as brain fluid accumulation, swelling, and microbleeds, which may necessitate hospitalization. Studies have not shown benefits from antibody treatments in patients with amyloid buildup but no symptoms.
There is no scientific evidence to support it,” stated Dr. George Perry, a neurobiologist and editor of the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Critics argue that the new criteria could significantly increase the pool of eligible candidates for new drugs, potentially resulting in substantial profits for drug manufacturers.
“The Alzheimer’s Association risks credibility by endorsing guidelines that classify perfectly healthy individuals as having Alzheimer’s disease,” remarked Dr. Adriane Fugh-Berman, director of PharmedOut, a Georgetown University program that monitors pharmaceutical marketing strategies.
If followed, these guidelines will ruin the lives of tens of thousands of people who will be misinformed that they have dementia,” she said. “The only entities that gain from this travesty are the pharmaceutical companies that make drugs for Alzheimer’s and the Alzheimer’s Association, which is preying on fear.”
The Alzheimer’s Association says its criteria is based on the latest developments in Alzheimer’s science. Because Alzheimer’s therapies haven’t been approved for people without symptoms, for now, it recommends against diagnostic testing in people without cognitive impairment, according to the working group that developed the criteria.
“Our goal in sharing them now — even as the field and our knowledge continues to evolve — is to advance diagnosis, treatment and prevention in order to improve individual care and reduce the societal impact of Alzheimer’s,” said Dr. Maria C. Carrillo, the Alzheimer’s Association’s chief science officer and medical affairs lead, and senior author on the new criteria.
Conflicts of Interest Regarding Financial Matters
The new criteria, developed by a 20-member working group from the leading patient advocacy organization for Alzheimer’s, have drawn attention due to financial conflicts of interest among its members. A significant portion of the panel, including a third directly employed by pharmaceutical companies and another third receiving payments from pharmaceutical or testing companies, has financial ties to entities involved in marketing or developing new Alzheimer’s drugs. Additionally, two panel members were Alzheimer’s Association employees, an organization that also accepts funding from pharmaceutical companies. Only a small number of members declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
We should question the reliance on guidelines influenced by industry,” stated Dr. Eric Widera, a geriatrician at the University of California San Francisco, who authored a commentary in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society on the new criteria.
Widera criticizes what he sees as a familiar pharmaceutical industry tactic: expanding the disease diagnosis to broaden the market for a drug. “This is diagnostic creep,” he emphasized.
He pointed to examples such as Abbott Labs’ “Is it low T?” campaign, which promoted a testosterone replacement product along with a more sensitive hormone test. Biogen’s “It’s Time We Know” campaign similarly raised awareness about mild cognitive impairment after the controversial FDA approval of its Alzheimer’s drug Aduhelm in 2021, which has since been withdrawn from the market.
Under the new criteria, Widera estimates that up to 1 in 10 healthy 50-year-olds could test positive for beta amyloid. While about 6 million Americans currently live with Alzheimer’s, projections suggest approximately 40 million could test positive for beta amyloid.
“These publications serve as part of a strategy aimed at maximizing sales of monoclonal antibodies,” remarked Dr. Karl Herrup, a neurobiology professor at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine.
Justifying Industry Participation in Guidelines Development
Dr. Clifford Jack, a brain imaging researcher at the Mayo Clinic, spearheaded the development of the new guidelines and expresses pride in the committee’s achievements.
I authored approximately 99% of the final document and have no conflicts of interest,” stated Dr. Clifford Jack.
The authors attribute the guideline change to advancements in Alzheimer’s disease treatment and new blood tests for amyloid and tau proteins. These tests, available through specialized labs, await FDA approval pending rigorous validation to minimize false results.
In a commentary published in Nature Medicine, the work group emphasized its diverse composition, including members from industry, clinical medicine, academia, FDA, and the National Institute on Aging. They aimed to integrate varied perspectives to reflect the latest scientific knowledge.
“We aimed to incorporate the best current scientific insights, including industry research, which conducts these trials,” Jack remarked. “Throughout the process, there was no effort by any committee member to promote commercial interests in these guidelines.
The initial draft of the criteria, introduced at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference in 2023, initially noted a collaboration between the Alzheimer’s Association and the National Institute on Aging. However, after facing criticism, the institute removed its name from the title following directives from the broader National Institutes of Health administration. This action was in adherence to an NIH policy against endorsing private entities, products, or services, as stated in an email from the National Institute on Aging.
The National Institute on Aging affirmed its continued participation in the working group and expressed its commitment to ongoing collaboration with the Alzheimer’s Association and other involved organizations.
Since the release of the draft criteria, the Alzheimer’s Association has clarified that they are not intended to serve as comprehensive diagnostic guidelines for clinicians. Instead, the criteria are positioned as a ‘bridge’ between research findings and clinical practice.
Development of Updated Guidelines Underway
The Alzheimer’s Association intends to assemble a fresh workgroup comprising different members to craft practical guidelines for diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease in clinical settings. The extent to which these guidelines will align with the diagnostic criteria remains uncertain.
According to Dr. Clifford Jack, the guidelines are expected to provide specific, actionable recommendations that may include references to particular commercial products.
Spokesperson Niles Franz affirmed the Alzheimer’s Association’s commitment to developing credible clinical practice guidelines and evidence-based recommendations to guide clinical decision-making at various levels, from individual to population health.
Franz emphasized that trustworthy guidelines, as outlined by the National Academy of Medicine, necessitate collaboration between organizing bodies and panels of experts who have minimal intellectual and financial conflicts.
The Association has recently implemented stringent protocols for collecting disclosures of conflict of interest from panel nominees, evaluating these disclosures, selecting members, and managing conflicts throughout and after guideline development,” he stated.
Franz expressed the association’s aim to finalize the new clinical guidelines for publication by 2025.
In the interim, Widera and others stress that the decision to use amyloid-clearing drugs is highly personal and should involve close consultation with a physician.
“There is arguably more controversy surrounding these guidelines than the drugs themselves,” noted Widera.
Looking ahead, Widera hopes the Alzheimer’s Association will address the risks in future guidelines.
“If the definition of a disease is broadened, it’s crucial to outline the associated risks and harms,” he emphasized.
Health & Wellness
Surprising Surge: ER Visits Soar for Heat-Related Illnesses in Unexpected Hotspots
Published
4 weeks agoon
June 27, 2024
As heat waves blanket parts of the US, hospitals across multiple states are grappling with a dramatic increase in heat-related emergencies, a trend highlighted by data from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Forecasters anticipate more unseasonably warm weather later this summer.
Interestingly, the regions hardest hit by heat illnesses, as indicated by the CDC’s data, are not necessarily those experiencing the highest temperatures. While the South and Southwest endure scorching temperatures exceeding 100 degrees Fahrenheit, it’s the Northeast, Mid-Atlantic, Midwest, and Mountain West—where temperatures range from the 80s to 90s—that are witnessing the highest numbers of heat-related ER visits. This heat is notably abnormal for mid-June, significantly surpassing historical averages.
For instance, this past Saturday marked a critical point, with hospitals in over two dozen states across six regions reporting “extremely high” rates of heat-related emergencies. These incidents are defined by the CDC as falling within the top 5% of the busiest days for heat-related illnesses observed from 2018 to 2023.
Heat Risks: Buildings and Inexperience
Claudia Brown, a CDC health scientist, explains that the built environments in these areas are ill-equipped to cope with heat, and people’s bodies are less acclimated to high temperatures.
“In more northern regions, for instance,” Brown, who works in the CDC’s National Center for Environmental Health’s Climate and Health Program, notes, “there tends to be lower prevalence of home air conditioning. This means that while temperatures may not reach the extremes seen in places like Arizona, the health impact can be greater due to inadequate infrastructure to manage heat.
Amid escalating climate change impacts amplifying both frequency and intensity of heat waves, the CDC introduced a new heat risk tool earlier this year. This online tool allows people to enter their ZIP code to access a heat forecast and receive safety recommendations.
Dr. Cheyenne Falat, an emergency department physician at the University of Maryland in Baltimore, has been witnessing a surge in severe heat-related cases over recent weeks, exacerbated by the city’s recent declaration of a code red heat alert. Cooling stations have been opened for residents in response.
“We’ve treated significant cases of heat stroke and other heat-related illnesses,” said Falat, who specializes in environmental medicine. She anticipates further challenges ahead.
In Baltimore, where substance use disorders are prevalent, individuals can face danger if they consume drugs and become incapacitated in unattended vehicles. Other patients include elderly individuals living in homes without air conditioning, outdoor workers, and individuals who underestimate the heat during outdoor activities.
Falat underscored the seriousness of heat as a health hazard, emphasizing that heat waves claim more lives, on average, than any other type of extreme weather events.
Surviving Extreme Heat: Safety Tips
Dr. William Brady, an emergency department physician at the University of Virginia Health System in Charlottesville, also attributes the issue to lack of experience.
If you live in New Hampshire, you’re generally not accustomed to coping with high heat periods,” noted Dr. William Brady, an emergency department physician at the University of Virginia Health System in Charlottesville. “People often don’t anticipate the need to be cautious in hot conditions.”
Dr. Brady highlighted an increase in cases of heat exhaustion at their ER, particularly among individuals who work or exercise outdoors. Symptoms typically include nausea, vomiting, headache, and similar discomforts.
While Dr. Brady hasn’t encountered any cases of life-threatening heat stroke so far, he cautioned that heat exhaustion can escalate to this severe condition. Symptoms of heat stroke include severe headache, rapid heart rate, high fever, confusion, and potential loss of consciousness.
He also noted a rise in patients with pre-existing health issues like emphysema, heart failure, and diabetes, conditions that heighten their vulnerability to heat-related complications.
“We’re definitely seeing more patients who are struggling to cope with the heat,” Dr. Brady added.
With climate change driving longer and hotter heat waves, Americans are facing a significant learning curve regarding heat dangers.
“We understand that high temperatures and humidity can be uncomfortable,” noted Brady. “But we’re not accustomed to perceiving it as a serious threat, unlike other regions of the world.”
Brady recently attended a medical conference in Taiwan where he took a course on managing large crowds and gatherings during extreme heat, aiming to reduce the risk of heat-related injuries.
“This is an emerging issue that we must address,” Brady emphasized. “It poses a considerable danger that demands our attention.
Health & Wellness
Controversial FDA Approval of Menthol E-Cigarettes Sparks Outcry from Anti-Tobacco Advocates
Published
1 month agoon
June 24, 2024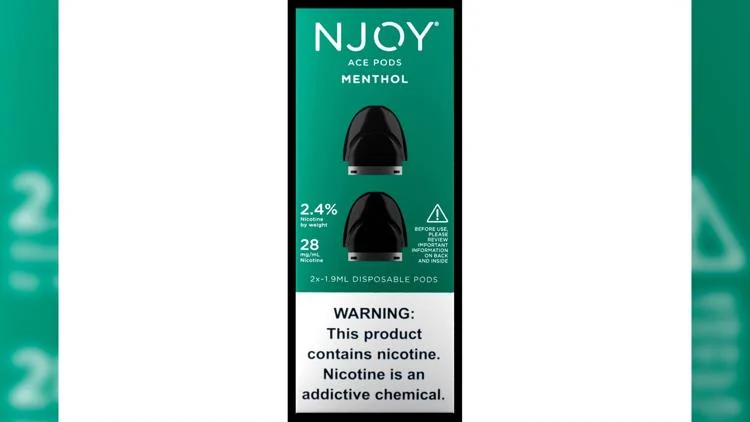
The US Food and Drug Administration granted approval on Friday to four menthol vaping products, marking the first time it has authorized e-cigarette products with flavors other than tobacco.
This decision has sparked strong criticism from pediatricians and anti-tobacco organizations, who argue that it undermines public health efforts and poses serious risks, especially to children.
The newly authorized products, manufactured by NJOY, a subsidiary of Altria, include disposable e-cigarettes and prefilled pods designed for use with the company’s reusable vaping device. These products contain nicotine levels ranging from 2.4% to 6%. CNN’s request for comment from the company went unanswered.
The US Food and Drug Administration emphasized that its recent authorizations of tobacco products, issued on Friday, do not equate to an endorsement of safety or FDA approval. The decision was based on evidence submitted by the manufacturer, indicating potential benefits for adult smokers seeking to switch from traditional cigarettes to e-cigarettes. The agency concluded that these products, despite concerns, could contribute positively to public health.
Dr. Matthew Farrelly, director of the FDA’s Center for Tobacco Products’ Office of Science, underscored in a press release that their scientific evaluation demonstrated enough evidence of harm reduction for adult smokers switching to less harmful alternatives.
Originally marketed by tobacco companies as a less harmful option than cigarettes and promoted for smoking cessation, e-cigarettes gained popularity with flavored varieties, which attracted young users. This led to a surge in youth vaping, prompting FDA scrutiny and restrictions on flavored products. Despite ongoing regulatory efforts, flavored e-cigarettes are still available as the agency reviews marketing applications.
Addressing the US Senate Judiciary Committee recently, an FDA official affirmed that regulating e-cigarettes remains a top priority. However, the agency faced challenges after a federal court ruling in 2021 compelled it to expedite the review process for e-cigarette makers’ applications, highlighting the need for stricter oversight under the Tobacco Control Act.
The FDA has been processing a massive backlog of 27 million applications from companies seeking approval to market e-cigarette products. So far, only 27 of these applications have been approved by the FDA, and until now, only tobacco-flavored products had received clearance.
Criticism swiftly followed Friday’s decision from anti-tobacco groups and medical professionals, who argued that it was shortsighted and posed significant risks, particularly for young people.
Yolonda C. Richardson, president and CEO of the Campaign for Tobacco-Free Kids, expressed bewilderment at the decision, questioning why the FDA would authorize flavored e-cigarettes despite acknowledging their appeal to youth and their role in the youth vaping epidemic. Richardson emphasized that the FDA should prioritize removing unauthorized and illegal e-cigarette products rather than permitting the sale of flavored options that could addict young people.
In response to the FDA’s move, the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network conveyed disappointment, describing it as detrimental to public health. This criticism comes amid ongoing delays in implementing a planned ban on menthol cigarettes and flavored cigars, which the Biden administration has yet to finalize.
Lisa Lacasse, president of the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network, criticized the FDA’s decision, noting that it follows the administration’s delay in finalizing rules to ban menthol in cigarettes and all flavors in cigars. She described the authorization of menthol-flavored e-cigarettes, including disposable options, as a missed opportunity for the FDA to prioritize public health. Lacasse argued that by allowing these products, the agency continues to enable Big Tobacco to addict another generation of youth, contrary to safeguarding public health and preventing lifelong addiction.
The American Academy of Pediatrics also expressed profound disappointment with the FDA’s move. Dr. Benjamin Hoffman, the president, emphasized the detrimental impact previous decisions allowing flavored e-cigarettes had on children and warned of the inevitable accessibility of these products to middle schoolers. He stressed that the FDA must swiftly reverse what he termed a deeply unwise decision once these products find their way into youth’s hands.
Erika Sward, assistant vice president of nationwide advocacy for the American Lung Association, underscored the organization’s opposition to any flavored e-cigarette products on the market. She highlighted the significant concern over the high nicotine levels of 5% and 6% in these newly authorized products, predicting increased addiction rates, especially among young people. Sward emphasized that menthol-flavored e-cigarettes, paired with such potent nicotine concentrations, present a dangerous combination that could lead to widespread harm.
According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, approximately 10% of high school students and nearly 5% of middle school students currently use e-cigarettes. The FDA reports a significant 60% decline in e-cigarette use among middle and high school students over the past five years. However, when teens and young adults do vape, they overwhelmingly prefer flavored e-cigarettes compared to adults.
The 2023 National Youth Tobacco Survey reveals that more than 23% of high school e-cigarette users across the country opt for menthol-flavored products.
To mitigate youth access and exposure, the FDA has implemented rigorous marketing restrictions on the newly authorized products. The agency emphasized its commitment to closely monitoring how these products are marketed. If the manufacturer fails to adhere to regulatory standards, the FDA reserves the right to suspend or withdraw its authorization.
The FDA reiterated its stance that all tobacco products pose harm and carry addiction risks. The agency strongly advises against initiating tobacco product use for those who do not currently use these products.
Health & Wellness
Addressing the Bird Flu Risk: Steps Forward for Greater Prevention
Published
1 month agoon
June 19, 2024
The United States’ delayed response to H5N1 bird flu, with reported cases in humans and cattle across several states, highlights critical gaps in coordination and readiness. Unlike Finland, which swiftly contained the virus in animals before human transmission, the U.S. faces challenges in timely detection and coordinated action. Efforts such as increased test production, vaccine evaluation, and wastewater monitoring show progress, but rapid response and integrated efforts between human and animal health sectors are crucial for effective containment and prevention. Strengthening these measures is essential to mitigate risks to public health and restore confidence in pandemic preparedness.
In the United States, H5N1 has been spreading among cattle since late last year, yet comprehensive testing and tracking have been insufficient to gauge its full extent among animals and humans. Advocates argue for adopting the 7-1-7 target for outbreak management: detecting suspected outbreaks within seven days, notifying authorities within one day, and completing the initial response within seven days to prevent further spread. Finland successfully adhered to this standard, unlike the U.S., where it took approximately 100 days to detect H5N1 in cattle, with uncertainties persisting over meeting the timely response target.
Trust is crucial in pandemic response. Finland’s established trust in its food authority facilitated swift action, including reimbursing farmers promptly for culling affected animals and launching a vaccination program for frontline workers against H5N1. Conversely, trust in the U.S. government remains low, particularly among rural communities affected by outbreaks. Efforts such as financial assistance to farms and support for veterinary expenses aim to bolster containment measures and rebuild confidence in public health initiatives. However, continued improvement in communication, coordination between human and animal health sectors, and proactive measures are essential to safeguard the agricultural sector and public health in the U.S.

“Effective Government Collaboration in Finland: Swift Action and New Laws Enhance Response”
Officials in Finland’s human health and agriculture sectors collaborated closely, leading to a rapid and efficient response. This joint effort bolstered detection capabilities, fostered collaboration among industry stakeholders, and prioritized worker protection from infection. Finland promptly enacted new legislation to empower effective control measures.
In the United States, governmental agencies face challenges due to differing priorities, legal mandates, flexibility, and political considerations. Multiple agencies, such as USDA for cattle health, FDA for milk safety, and CDC for human diseases including those from animal exposure, are involved. While coordination is improving, effective directives should be tailored to each community’s specific needs rather than relying solely on national mandates, given the country’s vast size and diversity.
There is a pressing need for enhanced collaboration among local, state, and federal authorities, including agencies like CDC, USDA, and FDA, as well as their state counterparts. Transparency and real-time information sharing with the public are essential. Congress must allocate resources to strengthen pandemic prevention and response systems, workforce readiness, and infrastructure. Crucially, building trust with farm owners and workers through responsive communication and support is paramount.
Effective responses to outbreaks like H5N1 require global cooperation, as microbes transcend borders. Our organization’s recent report underscores the importance of proactive health systems in preventing epidemics through meticulous planning, early detection, and decisive action.
Health & Wellness
Senators Demand Answers: FDA and DOJ Under Fire for Inaction on Youth Vaping Crisis
Published
1 month agoon
June 13, 2024
Rare Bipartisan Agreement in Senate Judiciary Committee Criticises FDA and DOJ for Failing to Address Youth Vaping Crisis
Three years after a federal court deemed FDA’s actions in violation of the Tobacco Control Act for permitting unapproved e-cigarette products, Senators express frustration as FDA misses deadline for review of e-cigarette makers’ applications.
A recent study reveals a concerning trend: approximately 2.1 million children have taken up e-cigarettes regularly since a pivotal federal court ruling three years ago. What’s more alarming is that the majority of these young users are attracted to flavoured e-cigarette products, raising concerns about their appeal to minors.
Senator Dick Durbin of Illinois sharply criticised the FDA for its sluggish response to this escalating crisis. He slammed the agency for failing to act decisively after missing the court-imposed deadline in September 2021, allowing unauthorised e-cigarettes to flood the market. Durbin’s frustration peaked when he discovered flavoured vapes being sold near the FDA headquarters, highlighting the audacity of their availability despite lacking FDA approval.
Dr. Brian King, director of the FDA’s Center for Tobacco Products, defended the agency’s enforcement priorities amidst mounting criticism. He cited the overwhelming influx of 27 million applications for e-cigarette products as a significant challenge, requiring careful allocation of resources.
However, Senator Marsha Blackburn of Tennessee expressed disappointment with the FDA and the Department of Justice representatives’ lack of a coherent plan of action. She emphasised the need for a clear strategy moving forward, expressing concern over the agencies’ seeming inability to chart a path forward in addressing the youth vaping epidemic.
One significant obstacle highlighted by Dr. King was the absence of a funding mechanism for the FDA’s oversight of the e-cigarette market. Unlike pharmaceutical and medical device companies, e-cigarette makers do not pay user fees to fund the agency’s regulatory efforts. This funding gap poses significant challenges for the FDA in effectively regulating the rapidly evolving landscape of e-cigarette products.
The changing landscape of tobacco products poses unprecedented challenges in terms of time and resources for the FDA, according to Dr. King. Despite this, the agency has authorised a mere 23 e-cigarette products since June, none of which are flavoured, while hundreds of thousands of applications await review. Senator Cornyn highlighted a staggering 1,500% increase in flavoured tobacco products sold in the US from 2020 to 2023, presenting flavoured vape products purchased by his staff as evidence of their appeal to children.
Dr. King acknowledged that flavoured varieties often attract youth consumers, with around 90% of e-cigarette users in this demographic opting for flavoured options. Although there has been a decline in overall e-cigarette use among middle and high school students over the past five years, flavoured e-cigarettes remain popular among teens and young adults.
The FDA and DOJ emphasised the enforcement challenges during the hearing, citing thousands of inspections and warning letters issued to manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. However, they admitted limitations in their authority, relying on collaboration with other agencies to combat illegal sales. Recently announced, a task force comprising multiple law enforcement entities will utilise criminal and civil measures to tackle the illicit distribution of e-cigarettes.
Dick Durbin, expressing frustration, directed a pointed question to Arun Rao of the Justice Department’s Consumer Protection Branch: ‘What have you been waiting for?’ Rao defended the department’s actions, citing collaborations with agencies like the US Marshals Service and the FDA to seize illicit products. However, Rao admitted to loopholes in the premarket authorization process, exploited by manufacturers who make minor alterations to resubmit their products. Overseas makers sometimes falsify shipments to bypass regulators, contributing to the accessibility of illegal e-cigarettes.
Concerns were raised about China’s ban on flavoured e-cigarettes, contrasting with their availability in the US, prompting criticism from Senator Cornyn. Dr. Susan Walley of the American Academy of Pediatrics highlighted the dangers of nicotine addiction among teens, emphasising its detrimental effects on brain development. She underscored the ease of access to flavoured products, presenting a purchased e-cigarette near a school as evidence.
Walley demanded swift action from the federal government to remove illegal products from the market. Even representatives from the vaping industry expressed dissatisfaction with the FDA’s authorization process.
Tony Abboud, representing the Vapor Technology Association, described the current situation as chaotic, emphasising the lack of a clear pathway through the approval process for vaping products. He warned that without a defined process, the market would continue to be flooded with illicit products.
A Seattle high school senior, Josie Shapiro, shared her firsthand experience with the committee, highlighting the ease of access to vaping products and their misleading perception of harmlessness due to enticing flavours and packaging. Shapiro revealed the impact of vaping on her life and that of her friends, expressing feelings of helplessness and isolation as they struggled to quit amidst addiction. She described how vaping dominated their thoughts and hindered their ability to enjoy quality time together.
Health & Wellness
FDA Issues Warning: ‘Microdose Chocolate’ Linked to Hospitalizations.
Published
2 months agoon
June 11, 2024
The FDA cautions both consumers and retailers against consuming, selling, or offering for sale any microdosing chocolate bars from the Diamond Shruumz brand due to multiple hospitalizations reported across four states.
According to an advisory from the FDA, eight individuals have reported feeling unwell after consuming chocolates from Diamond Shruumz. Among these cases, six people required hospitalisation. The affected individuals are distributed across four states: four in Arizona, two in Indiana, one in Nevada, and one in Pennsylvania.
The FDA stated that individuals who ingested the chocolate bars have reported various symptoms, such as seizures, central nervous system depression (manifested as loss of consciousness, confusion, and drowsiness), agitation, irregular heart rates, high and low blood pressure, as well as nausea and vomiting.
There have been no reported fatalities associated with the consumption of these products.
Micro-dosing involves the practice of consuming minimal amounts of psychedelic substances such as psilocybin mushrooms. Advocates of micro-dosing claim that these small doses can enhance mood and focus.
As per information provided on the company’s website, Diamond Shruumz’s chocolate bars are crafted using a unique combination of nootropic and functional mushrooms. It’s emphasised that these products do not include substances like psilocybin, amanita, or any regulated drugs.
CNN has attempted to reach out to Diamond Shruumz for comment but has not received a response at the time of publishing.
Despite the FDA’s advisory, Diamond Shruumz has continued to share promotional content on their Instagram and TikTok profiles without acknowledging the reported illnesses.
If you or someone you know experiences symptoms after consuming Diamond Shruumz’s chocolate bars, the FDA advises consulting a healthcare provider and/or contacting the Poison Help Line at 1-800-222-1222.
Health & Wellness
WHO Chief Scientist Urges Heightened Surveillance and Readiness for Severe Avian Influenza
Published
3 months agoon
April 22, 2024
In response to the escalating threat of highly pathogenic bird flu, the World Health Organization’s Chief Scientist has issued a compelling call to action. Emphasizing the critical need for heightened surveillance and readiness, the WHO aims to mobilize global efforts in combating this potentially devastating disease.
Avian influenza, commonly known as bird flu, poses a significant risk to both animal and human health. With recent outbreaks causing concern among health officials worldwide, proactive measures are essential to prevent further spread and mitigate potential outbreaks.
The WHO’s Chief Scientist, a prominent figure in global health policy, has underscored the urgency of the situation. Through increased surveillance, early detection, and rapid response mechanisms, countries can effectively identify and contain outbreaks before they escalate into larger-scale crises.
Furthermore, the WHO emphasizes the importance of preparedness efforts, including stockpiling antiviral medications, enhancing laboratory capabilities, and strengthening healthcare systems. These proactive measures are crucial in minimizing the impact of avian influenza on both human and animal populations.
In addition to governmental action, the WHO calls for collaboration among international organizations, research institutions, and the private sector. By pooling resources and expertise, the global community can more effectively address the complex challenges posed by avian influenza.
The WHO’s proactive stance reflects a commitment to safeguarding public health and preventing the spread of infectious diseases. As the threat of severe avian influenza persists, the organization remains steadfast in its efforts to protect communities worldwide.
In conclusion, the WHO’s Chief Scientist’s call for heightened surveillance and readiness serves as a crucial reminder of the ongoing threat posed by avian influenza. By prioritizing vigilance and preparedness, the global community can work together to mitigate the risks and protect public health.
Trending
-

 Entertainment3 years ago
Entertainment3 years agoEva Savagiou Finally Breaks Her Silence About Online Bullying On TikTok
-

 Entertainment2 years ago
Entertainment2 years agoTraumatone Returns With A New EP – Hereafter
-

 Entertainment2 years ago
Entertainment2 years agoTop 5 Influencers Accounts To Watch In 2022
-

 Fashion3 years ago
Fashion3 years agoNatalie Schramboeck – Influencing People Through A Cultural Touch
-

 Fashion3 years ago
Fashion3 years agoThe Tattoo Heretic: Kirby van Beek’s Idea Of Shadow And Bone
-

 Entertainment3 years ago
Entertainment3 years agoTop 12 Rising Artists To Watch In 2021
-

 Entertainment3 years ago
Entertainment3 years agoMadison Morton Is Swooning The World Through Her Soul-stirring Music
-

 Entertainment3 years ago
Entertainment3 years agoTop 10 Influencers To Follow This 2021
-

 Entertainment3 years ago
Entertainment3 years agoBrooke Casey Inspiring People Through Her Message With Music
-

 Entertainment3 years ago
Entertainment3 years agoFiery, Electric, And Tenacious. Leah Martin-Brown’s All That

